Michael MacLafferty | Oakland Therapist
My first article for Psyched Magazine! It is a personal piece that I hope interests and resonates with others.
Michael MacLafferty | Oakland Therapist
My first article for Psyched Magazine! It is a personal piece that I hope interests and resonates with others.
Three victories in the appellate-level courts in the last week is great news. Two are transgender student cases — Gloucester County School Board v. G.G. in the 4th Circuit Court of Appeals and a similar case from DC (see Grace Dolan-Sandrino’s story from her viewpoint).
The third case is a sex-discrimination case in employment. In this case, a lesbian — Kimberly Hively —successfully argued before the 7th Circuit Court of Appeals that Ivy Tech Community College fired her because she’s a lesbian and this firing was a form of sex discrimination because she is a lesbian. Judge Diane Wood wrote the court decision affirming that there was sex discrimination because the community college based the firing decision on Ms. Hively’s “gender non-conforming” behavior. This form of “gender stereotyping falls within Title VII’s prohibition against sex discrimination” and is thus a clear case of sex discrimination according to Judge Wood.
Since these cases are all at the lower court level and other appellate courts have come to differing decisions, these cases and similar ones could end up at the US Supreme Court. But for now, SUCCESS on these types of LGBTQIA cases related to education and employment have occurred within some parts of the country. We’ll just have to wait and see what the final outcome will be.
We’ll just have to wait and see what the final outcome will be.
On the surface, last week’s court case about Gavin Grimm looked like a loss for human rights. When the Gloucester County (VA) School Board banned transgender students from using the bathrooms that conformed with their gender identities, Gavin Grimm, then 15, addressed the board on November 11, 2014 to explain why he was not a threat to other students. The transgender teen explained that he had used the boys’ bathroom in public places throughout Gloucester County and had never had a confrontation. As Seth Millstein wrote:
“He explained that he is a person worthy of dignity and privacy. He explained why it is humiliating to be segregated from the general population. He knew, intuitively, what the law has in recent decades acknowledged: the perpetuation of stereotypes is one of many forms of invidious discrimination. And so he hoped that his heartfelt explanation would help the powerful adults in his community…
View original post 1,384 more words
Since I started this blog in December 2012, I have annually written about pay equity during April for Pay Equity Day (2013, 2014, 2015, and 2016). That day is today. As in past years, Ni-Ta-Nee NOW, the local chapter of the National Organization for Women, will be distributing flyers educating the public about the economic inequality in women’s pay. We’re letting people know that we continue to have a lack of progress in eliminating pay inequity. Here’s the information we would like the public to know.
This date symbolizes how far into the year a woman must work, on average, to earn as much as a man earned the previous year according to the National Committee on Pay Equity. FYI, This is eight days less than 2016, ten days less than 2015, four days less than 2014, eleven days less than in 2013 and thirteen days less than in 2011 when Ni-Ta-Nee NOW started tracking this date! Tuesday, April 4, 2017, is the day on which women’s wages overall catch up with men’s earnings from the previous year. It is also the day when white women’s wages catch up with men’s wages. But most women of color take much longer to achieve equity.
A Nationwide View of the Gender Wage Gape
The commonly used measure to determine the pay gap is the ratio of women’s to men’s median annual earnings for full-time, full-year workers. Based on these earnings, women as a whole earned just 8 percent of what men earned in 2015 (AAUW, 2017). Between 2006 and 2015 the weekly gender wage gap narrowed by just 0.3 percentage points, compared with 6.0 percentage points in the previous ten years (1996 to 2005). At the current rate, it will be 2059 before women achieve wage parity. This lack of progress needs to be overturned!
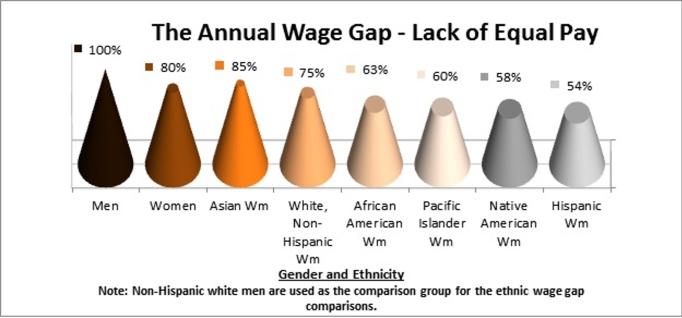
Nationally, Asian American women have the smallest wage gap, earning 85 percent of what the average white man earned in 2012. White, non-Hispanic women are next, earning approximately 75 percent of white men’s average income, African-American women earn 63 percent, Pacific Islander women earn 60 percent, Native American women earn 58%, and Hispanic women earn just 54 percent of wages as compared to white men (AAUW, 2017).
A woman who is just starting her career now will earn $418,800 less than her male counterpart over the course of a 40-year career. For Asian-American women, it’s $387,640; for white, non-Hispanic women, it’s $462,000; for African-American women, it’s $657,680, for Native American Women, it’s $789,120, and for Hispanic women, it’s $899,400. (NWLC, 2017).
Differences in the wage gap are due more than just the types of jobs men and women work. Part of the problem is due to gendered, sex-segregated jobs where women are paid less. This disparity is partly due to the minimum wages often paid to women and for jobs that require the same level of skills, knowledge & abilities but for which women are paid less. Other reasons for this pay gap include the lack of paid sick days and family leave, unfair scheduling practices, and lack of pay transparency protections in these female-dominated occupations (Center for American Progress, 2015).
The pay gap is even worse in our state. When ranked among the other 50 states plus the District of Columbia, Pennsylvania’s wage gap placed it 27th (tied with AR, IL, NE, TX, and WA) among the states (AAUW, 2017). The median annual income for a woman working full-time, year-round in Pennsylvania in 2015 was $40,742 compared to men’s $51,212 or 80% of what a man earns. This disparity results in a wage gap of 20%.
Centre County is part of Pennsylvania’s 5th Congressional District (CD). Women in the 5thCD earned $33,325 compared to the $45,385 that men make or 73.4% of what a man makes. We rank 15 out of 18 in the state in terms of the wage gap. This disparity results in a wage gap of 26.6%. Philadelphia’s 1st CD fares better than the rest of the state, with a difference of just 11.3% (AAUW, 2017).
A woman who is just starting her career now will earn $430,480 less than her male counterpart over the course of a 40-year career. For Asian-American women, it’s $387,640; for white, non-Hispanic women, it’s $462,000; for African-Americans, it’s $657,680; for Native American women, it’s $789,120; & for Hispanic women, it’s $899,400 (NWLC, 2017).
If you are an employer, you can get help in examining pay practices by conducting an equal pay self-audit using the guidelines from the US Department of Labor (available at www.pay-equity.org/cando-audit.html).
Tell your employer if you see or think that you are being paid less than your male co-workers. Click here for some tips on negotiating for pay equity.
If there’s a union at your place of work, ask for their help.
If discrimination persists: There are three places to file complaints – at the federal level, at the state level, and at the local level.
You can file under federal law with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). Go to this link and follow the instructions.
You can find your state’s anti-discrimination agency website and contact information through the Job Accommodations Network, a free service of the U.S. Department of Labor’s Office of Disability Employment Policy. Most of the agencies have a website address that you can copy and paste into your browser. All of the agencies have a phone number that you can call for assistance.
If you live in Pennsylvania, you can file a complaint with the PA Human Relations Commission in Harrisburg. Contact information is available by region. Just go to their website and look for your county’s name. The phone number and address for your regional office is listed directly above the names of the counties served by each office.
You should also check to see if your local county, city, or community has an ordinance providing similar protections for wage-based discrimination. You can also file under federal law with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC).
There are a few communities throughout the country that have created local ordinances that include the state-based anti-discrimination protections and have also expanded coverage to other areas (such as protections based on sexual orientation, family status, and family responsibilities across the lifespan). If so, you can more conveniently file a wage-based complaint at the local level. Check with your state’s anti-discrimination agency to see if there is a local ordinance in your community.
In Pennsylvania, there are about 30 cities and municipalities with such an ordinance. Your regional office of the Pennsylvania Human Relations Commission can give you this information, along with whom to contact. Check with your state’s anti-discrimination office if you live in another state to determine if your state allows such local ordinances and if such a law exists in your community.
There are bills before Congress and in state legislatures that deal with some of the issues affecting wage inequity. If you want to advocate at the federal level, you can find your US Representative and your US Senators’ contact information at https://www.congress.gov/members. To locate the contact information for your state legislators, go to http://openstates.org/find_your_legislator/ and fill in your mailing address and hit the “locate” button; your legislators’ picture, addresses, and phone and fax numbers can be found when you click on her/his name. It some cases, this website will also provide a list of bills your legislator has sponsored so that you can see if one or more of them support pay equity.
Here are the issues you for which you should consider advocating. Since I live in Pennsylvania, I’m listing both Federal and Pennsylvania-specific bills. For bills specific to your state, check out the National Conference of State Legislatures website to find and go to your state’s website. You will then be able to search for the bills on pay equity, paycheck fairness, minimum wage, sick leave, etc. to see if there is a bill or law in your state addressing these issues. If not, then contact your legislators/public officials and ask them to sponsor such bills.
At the federal level, there is currently one bill addressing this issue. It is HR 122 — The Original Living Wage Act of 2017. It was introduced by Rep. Al Green (D-TX-9). There are currently seven additional co-sponsors: Rep. Elijah E. Cummings (D-MD-7), Rep. Eleanor Holmes Norton (D-DC-At Large), Rep. Gwen Moore (D-WI-4), Rep. Barbara Lee (D-CA-13), Rep. John Lewis (D-GA-5), Rep. Hakeem S. Jeffries (D-NY-8), and Rep. Marc A. Veasey (D-TX-33). For this bill to move, MANY more co-sponsors are needed and your representatives need to hear from you.
In Pennsylvania, there are two bills —SB 12 — Raising the Minimum Wage and Modernizing the Minimum Wage Act & SB 163 —Raising the Tipped Wage Act.
Many states and local communities have either increased the minimum and tipped wages or have bills in the hopper on this issue. According to the Raise the Minimum Wage website, “As a result of Congressional gridlock and growing income inequality, a record number of states are taking action to raise their wage floors above the federal [level]. Twenty-nine states, plus the District of Columbia, have set their minimum wage above $7.25/hour, including two which have raised it to $15 (California and New York). And in several other states, advocates are actively promoting an increase in the wage floor to at least $12. For more information on these types of bills, check out the Raise the Minimum Wage website for their listing of state-level initiatives.
At the federal level, check out HR 1022 and S 362 — the Federal Employees Paid Parental Leave Act of 2017. Note these bills only affect federal employee sick leave. So to create paid sick leave for the rest of us, we’ll need to look to the states and local municipalities for this form of legislation.
In Pennsylvania, check out HB 701 — the Pennsylvania Paid Sick Leave Act and SB 207 — the Employee Paid Sick Leave Act
In some states, this type of legislation can also be enacted at the municipal level. Currently, four states (Connecticut in 2011, California in 2013, Massachusetts in 2014, and Oregon in 2015) and the District of Columbia (2008), as well as 18 cities and communities, have implemented paid sick leave. These 18 cities (with the year of passage noted) are:
Types of paycheck fairness rules include limiting occupational requirements to bona fide occupational factors like education, skills, and experience, prohibiting employer retaliation against employees who discuss their salaries and denies employers the ability to require employees to sign a contract or waiver prohibiting them from disclosing information about the employee’s wages. The federal bills that have focused on this issue entitled the Paycheck Fairness Act; this bill has yet to be introduced in either the US House or Senate so far this year. The National Women’s Law Center has several good articles on paycheck fairness, including why women need more wage protections and information on how the Paycheck Fairness Act strengthens the Equal Pay Act. Take a look at these articles and then contact your US Senator(s) and your US Representative if you believe they might be willing to take the lead on this bill. FYI, the past prime sponsors of this bill that are still in Congress are Senator Patty Murray (D-WA) and Representative Rosa DeLauro (D-CT-3).
So, on this Equal Pay Day, get going! Follow the lead of the millions of women and their allies who participated in the Women’s Marches on January 21, 2017. Stand up! Fight back! Call on your legislators at all levels to work towards pay equity. Tell your employer/union that you want and expect fair pay. And reach out to others of like mind. This pull for equal pay will be a long haul effort. But we can eventually make it happen. Let’s do it!.
Poetry that speaks volumes!
Ableism is
when you say that I don’t act
disabled
and expect me to take that
as a compliment.
Ableism is
when you assume
that I’m automatically strong
and courageous
simply because I’m disabled.
Ableism is
when my blindness becomes
your darkness…
when you wear my scars
in your sleeve
and pretend to understand
my truths.
Ableism is
when you try to heal me,
and fix me
and promise me that I will walk,
or see, or hear
or that I will be
everything I was really meant to be…
one day
in heaven.
Ableism is
believing that heaven
is an able-bodied place
where broken bodies finally
become whole.
Ableism is
when “whole”
is a word reserved
for the able-bodied, or
when you say that I’m beautiful
despite my differences,
and fail to recognize that I’m beautiful
because of them.
Ableism is
when you leave us to ripen
and rot
View original post 1,640 more words
Other than the fallout from failing to pass Trumpcare and the increasing—and damning—news about Dictator Donald Trump’s (DDT) connection to Russia, the biggest news was his rollback to President Obama’s orders regarding the climate.
Climate: DDT ordered the EPA to repeal the Clean Power Plan by removing new limits on emissions from coal-fired power plants. He claimed that it was for the economy, energy security, and jobs, but the entire coal industry employs fewer people than Arby’s. DDT is preening, but the provisions weren’t to take place until 2022. In addition, a 2007 Supreme Court ruling found that greenhouse gases count as a potential air pollutant, requiring the EPA to regulate them. DDT’s order won’t reverse the decline of the coal industry that has fewer employees than clean energy. Coal’s enemy is natural gas.
Conflicts of Interest: Remember DDT’s blind trust to avoid conflicts of interest? Middle son, Eric, has…
View original post 1,348 more words
DIY Resource for those wishing to have their Italian citizenship recognized through Italy's "jure sanguinis" birthright citizenship & “Jure matrimonii” by marriage
We Make Scrapbooking Fun!
Pracademic | Climate & Sustainability | Democracy, Education & Policy | Creative & Mindful Living
Exploring the spidery corners of a culture and the weird stuff that tourist brochures ignore.
Big thoughts + big feels
Never doubt that a small group of thoughtful, committed citizens can change the world. Indeed, it is the only thing that ever has. -- Margaret Mead
Yet Another Attempt to Make the World a Better Place by Writing Things
Crescat Scientia Vita Excolatur
Progressive commentary from Gainesville, Florida, once called the Berkeley of the South. Potano was the chief of and the only known name of the Native American tribe inhabiting the area around what is now Gainesville at the time the Europeans arrived.
We have the right to remain silent. We just choose not to...
“It takes no compromise to give people their rights…it takes no money to respect the individual. It takes no political deal to give people freedom. It takes no survey to remove repression.” – Harvey Milk
she thinks. she says. she writes.
Working towards global equity and equality
One woman living a free and happy life
THE VOICE OF THE VOICELESS. Defending Human Rights. Promoting the Humanitarian spirit...
The main thing is to keep the main thing the main thing.
https://thehumanmirror.wordpress.com
Beating Back The Patriarchy Everday | 2009 - 2018
Distinguished individuals making a global impact
Indulge- Travel, Adventure, & New Experiences
draws comics
a feminist habit. thinking broadly about life and art. at peak. sometimes broadspoken. not a translation program. crushing the doublespeak. seeking free speech.
Curating nostalgia one memory at a time | Email: nilofar.haja@gmail.com
Energize! Organize! Stop the War on Women!
Political Co-Dependency Intervention
My life in art and the local community and everything in between
Adventures between cultures
Not a "how to be a great parent" blog
real world issues, religion, social causes, awareness, life in general
Progressive political commentary/book reviews for youth and adults
"We're About The Children, it's about time." (800) 787-4981
The views depicted here are my own, do not represent the views of anyone/anything else, and cannot be reproduced in whole or in part without my express written consent.
International Economic Affairs & Relations / Regional & International Organizations / Global Commerce & Business
Author. Speaker. Librarian.
It's all about disbelieving your thoughts
Learn more about the state laws being introduced and passed around the U.S. that is limiting Women's rights. Did you know that the Women's Equal Right Amendment from 1983 still needs to be ratified by 3 more states before it goes into effect?
Feminism, Writing, Activism